接着记录leetcode问题:
1002, 4, 215, 88, 674, 950
提炼技术:
- 记录字符频数
- 实时更新
- 额外变量
- 逻辑中由插入操作,考虑使用队列
#1002
描述
1
2
3找到单词的共有字符:
Input: ["bella","label","roller"]
Output: ["e","l","l"]思路
假设输入单词的列表是:[‘bcdc’, ‘dcc’, ‘cddcb’]
过程如下:loop:对于每一个单词记录其中字母出现的频数count,根据这个count,更新count26。 当所有单词统计过后,count26就包含了最终每个单词共有的字符出现的频数。 最后一步:将count26中频数大于0的字母放入res数组。其中,count26把元素初始化为可能的最大值;而且是个全局变量,对于每个单词都实时更新其值,节省了空间。
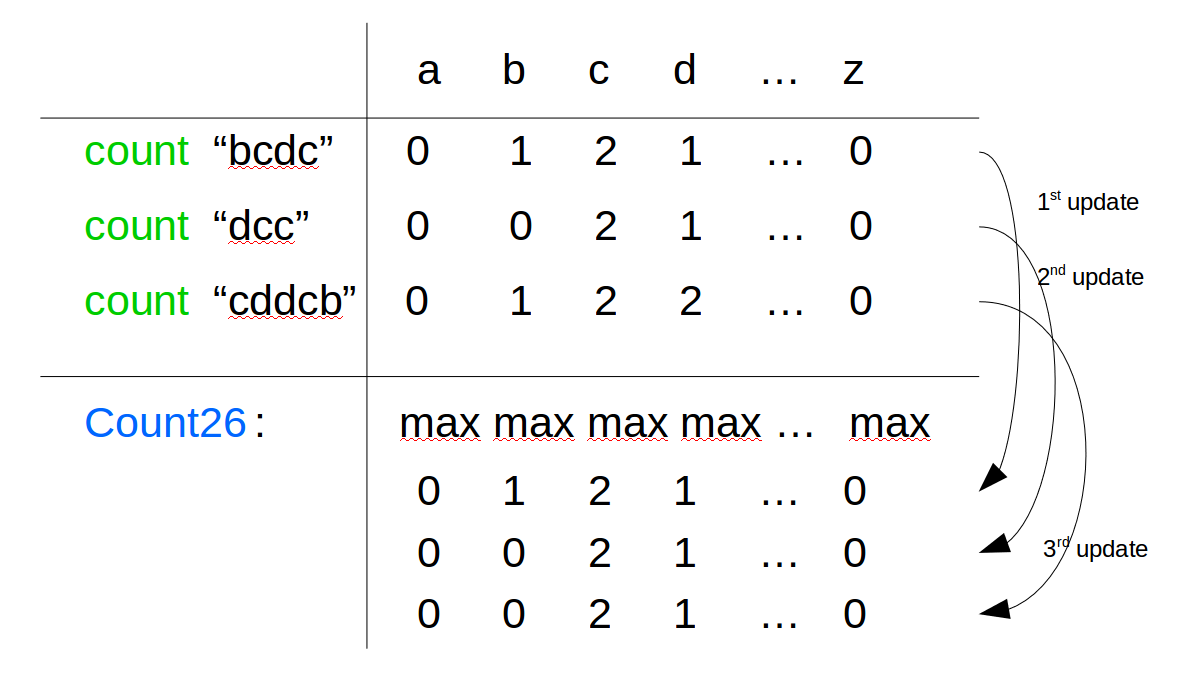
最终返回两个c一个d:[‘c’,’c’,’d’]。
看图说话
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22vector<string> commonChars(vector<string>& A){
vector<int> count26(26, INT_MAX);
vector<string> res;
for (auto word: A){
// 统计每个单词中每个字母出现的频数
vector<int> count(26, 0);
for (auto chara: word){
count[chara - 'a']++;
}
// 每一个单词统计频数后更新count26
for (int i=0; i<26; i++){
count26[i] = min(count26[i], count[i]); // online update
}
}
// 最终的count26中记录了每个字母出现的次数
for (int i=0; i<26; i++)
for (int j=0; j<count26[i]; j++)
res.push_back(string(1, i+'a')); // 索引0对应‘a’
return res;
}
关键:记录字符频数,实时更新,
#4 Median of Two Sorted Arrays
描述
1
2
3
4
5
6There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays.
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
思路
思路直接:第一步:merge两个有序数组,第二步:找到median。
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size();
int n = nums2.size();
// aux 数组记录merge后的数组
vector<int> aux(n+m ,0);
// merge two sorted arrays
int i=0,j=0,k=0;
for (k=0; k< m+n; k++){
// 如果i超过了nums1的长度,表示nums1中元素遍历完毕
if (i>=m)
aux[k] = nums2[j++];
// 如果j超过了nums2 的长度,表示nums2中元素遍历完毕
else if (j>=n)
aux[k] = nums1[i++];
// 如果两个数组都没有遍历完毕
else if(i<m && j<n && nums1[i] < nums2[j] )
aux[k] = nums1[i++];
// 如果两个数组都没有遍历完毕
else if (i<m && j<n && nums1[i] >= nums2[j] )
aux[k] = nums2[j++];
}
// 计算中间两个数的median
double res = 0;
if((m+n)%2 == 0)
res = 0.5*(aux[(m+n)/2] + aux[(m+n)/2-1]);
else if((m+n)%2 == 1)
res = (aux[(m+n)/2]);
return res;
}其实在后两个if else语句中的
i<m && j<n是多余的,因为,如果执行到了这里,i<m && j<n就已经满足了。
关键:merge操作的情况要考虑清楚,所有情况要完备且neat,功能实现无误后,将冗余的删除。
#215 Kth largest element
描述
1
2Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output: 5逻辑
当数组中的元素可以是任何整数时:
先排序,后直接取第k个元素(no good)
当数组中的元素中只含有0~9这10个,可以有其他方法:
使用频数数组记录每个digit出现的次数,根据这个频数与k的关系取到最终值。
一般的方法:
Top-k 问题,使用冒泡排序,秩序要冒泡k次。
实现
第一种情况:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10struct Increase{
bool operator()(const int& a, const int& b){
return a>b;
}
};
int findKthLargestElement(vector<int>& nums, int k){
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), Increase());
return nums[k-1];
}第二种情况可以使用如下方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18int findKthLargestElement(vector<int>& nums, int k){
int res = 1; // 与k比较
int count[10] = {0}; // 频数记录
for (int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){
count[nums[i]]++;
}
for (int i=9; i>=0; i--){
if (count[i] == 0) continue;
for (int j=1; j<=count[i]; j++){
if (res < k) res+=1;
else if(res == k) return i;
}
}
throw invalid_argument("no return");
}
#88 Merge Two Array
描述
1
2
3
4
5
6
7Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
NOTE: num1&num2 are sorted逻辑
其实就是实现Merge Sort的一个树结点的操作
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14vector<int> merge2(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {
int i=0; //def num1 的index
int j=0; //def num2 的index
int k=0; //def 结果array的index
vector<int> arr(m+n);
while(i<m || j<n){
if(nums1[i] <= nums2[j])
arr[k++] = nums1[i++];
else
arr[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
return arr;
}
#674 最长连续递增子序列的长度
描述
1
2
3比如:nums=[1,3,7,5,6,8,9]
返回4. 最长递增子序列是[5,6,8,9]逻辑
用变量
start标记每个递增子序列的第一个数的索引。
遍历nums数组,只要nums[i]<=nums[i-1],更新start为当前索引i。
i每次加1,res更新一次:res=max(res, i-start+1).实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10int func(vector<int>& nums){
int res = 0;
int start = 0; // extra variable
for (int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
if(i>0 && nums[i]<=nums[i-1])
start=i;
res = max(res, i-start+1); // update
}
return res;
}关键: 额外变量,实时更新,先手动实现,
#950 Reveal Cards In Increasing Order
描述
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21给出一个序列,含若干个元素,任意顺序,现在确定一种顺序S,使得这个顺序的序列执行如下操作的过程中,第一步取出元素为递增顺序。这个操作如下:
1. 取出序列的第一个元素
2. 如果此时序列中还有元素,将第一个元素放到序列尾部。
3. 只要序列中有元素,就执行1,2步骤。
返回S。
例:
Input: [17,13,11,2,3,5,7]
Output: [2,13,3,11,5,17,7]
Explanation:
We get the deck in the order [17,13,11,2,3,5,7] (this order doesn't matter), and reorder it.
After reordering, the deck starts as [2,13,3,11,5,17,7], where 2 is the top of the deck.
We reveal 2, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [3,11,5,17,7,13].
We reveal 3, and move 11 to the bottom. The deck is now [5,17,7,13,11].
We reveal 5, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [7,13,11,17].
We reveal 7, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [11,17,13].
We reveal 11, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [13,17].
We reveal 13, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [17].
We reveal 17.
Since all the cards revealed are in increasing order, the answer is correct.逻辑
既然初始序列
deck是任意的,所以先排序,从大到小排序得到新deck。过程中需要插入序列第二个位置,所以考虑使用双端队列为容器
dq。把第一个元素放入队列,从第二个元素开始。- 第一步 将队列的最后元素插入队列的第一个位置。
- 第二步 将当前序列中的元素
deck[i]插入队列首。 - 第三步 将此时的队列中最后元素删除。
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15vector<int> deckRevealedIncreasing(vector<int>& deck){
sort(deck.begin(), deck.end(), [](int& a, int& b)->bool{
return a>b;
});
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_front(deck[0]);
for (int i=1; i< deck.size(); i++){
dq.insert(dq.begin(), *(dq.end()-1));
dq.push_front(deck[i]);
dq.pop_back();
}
return vector<int>(dq.begin(), dq.end());
}
关键: 已知结果求原因,反推过去,
逻辑中由插入操作,考虑使用队列、
双端队列常用方法: push_front(), push_back(), pop_back(), pop_front(), insert()